The high-voltage battery is charged using a charging cable.
The battery can also be charged at charging stations using the integrated charge module. The charging stations can be equipped with either a fixed charging cable or a socket in which a special charging cable with a matching connector (a mode 3 charging cable) can be plugged in.
Rapid charging
In addition to charging via a 120/240 V outlet (alternating current), the vehicle also supports direct-current rapid charging at charging stations supporting the CCS (Combined Charging System) standard. Charging with direct current usually enables higher charging output and thereby shorter charging times. The highest charging output is normally achieved when the charge level of the high-voltage battery is 0-80%. When the charge level rises, the output will be decreased to reduce wear.
Warning
California Proposition 65
Operating, servicing and maintaining a passenger vehicle can expose you to chemicals including engine exhaust, carbon monoxide, phthalates, and lead, which are known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. To minimize exposure, avoid breathing exhaust, do not idle the engine except as necessary, service your vehicle in a well ventilated area and wear gloves or wash your hands frequently when servicing your vehicle. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/passenger-vehicle.
Note
Warning
The high-voltage battery's charging time depends on the charging output used.
Note
Warning
Charging cable handle and charging socket
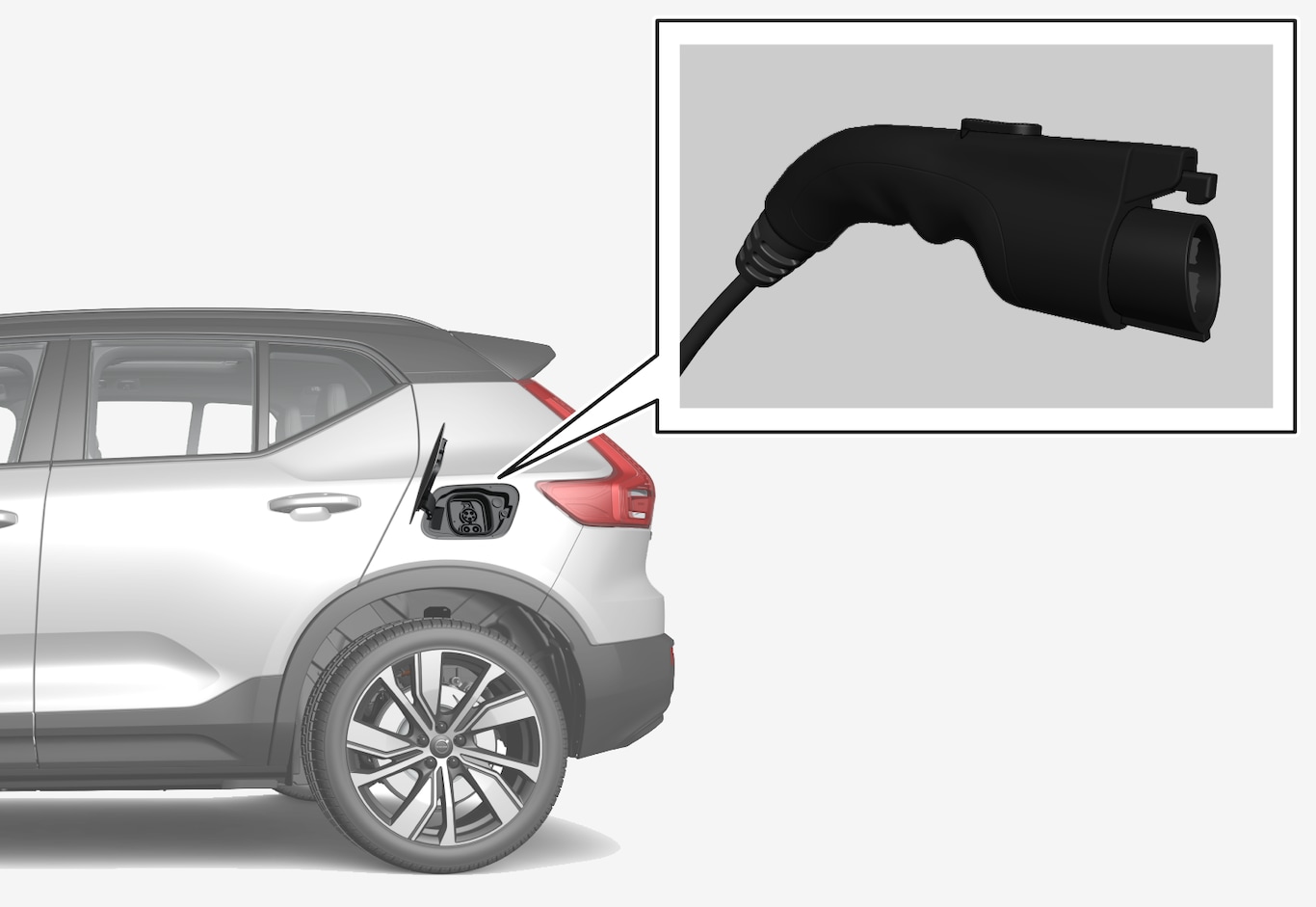
- indicator on the charging cable's control module
- indicator light in the vehicle's charging socket.
- images and text in the instrument panel.
The vehicle cannot be driven while it is being charged.
The high-voltage battery may have reduced performance if the temperature in the battery is too low or too high.