How Pilot Assist works
The Pilot Assist function is primarily intended for use on highways and other major roads where it can help provide a more comfortable and relaxing driving experience.
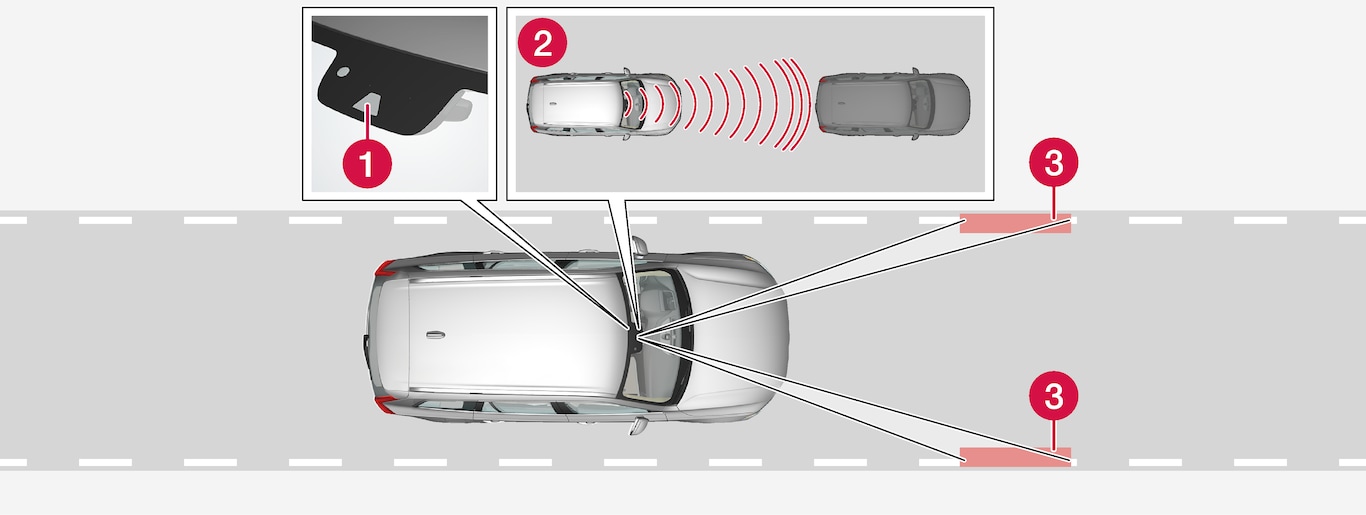
 Camera and radar sensor
Camera and radar sensor Distance monitor
Distance monitor Lane marker line monitors
Lane marker line monitors
The driver sets the desired speed and distance to the vehicle ahead. Pilot Assist monitors the distance to the vehicle ahead and the traffic lane's side markers using the camera and radar sensor. The system maintains the set time interval to the vehicle ahead by automatically adjusting your vehicle's speed and keeps your vehicle in its lane by providing steering assistance.
Pilot Assist's steering assistance is based on monitoring the direction of the vehicle ahead and the traffic lane's side marker lines. The driver can override Pilot Assist's steering recommendations at any time and steer in another direction, e.g. to change lanes or avoid obstacles on the road.
If the camera/radar sensor cannot detect the lane's side marker lines or if Pilot Assist is unable for some other reason to clearly interpret the lane, Pilot Assist will temporarily deactivate steering assistance until it can once again interpret the lane markings. However, the speed and distance warnings will remain active.
Warning

The color of the steering wheel symbol indicates the current status of steering assistance:
• GREEN indicates that steering assistance is active
• GRAY (as shown in illustration) indicates that steering assistance is deactivated.
Warning
- The Pilot Assist function is supplementary driver support intended to facilitate driving and help make it safer – it cannot handle all situations in all traffic, weather and road conditions.
- The driver is advised to read all sections in the Owner's Manual about this function to learn of its limitations, which the driver must be aware of before using the function (see the link list at the end of this article).
- Pilot Assist should only be used if there are clear lane lines painted on each side of the lane. All other use will increase the risk of contact with nearby obstacles that cannot be detected by the functions.
- Pilot Assist is not a substitute for the driver's attention and judgment. The driver is always responsible for ensuring the vehicle is driven in a safe manner, at the proper position within the lane, at the appropriate speed, with an appropriate distance to other vehicles, and in accordance with current traffic rules and regulations.
Note
Pilot Assist regulates speed by accelerating and braking. It is normal for the brakes to emit a slight sound when they are being used to adjust speed.
Pilot Assist attempts to smoothly regulate speed. The driver must apply the brakes in situations requiring immediate braking. For example, when there are great differences in speed between vehicles or if the vehicle ahead brakes suddenly. Due to limitations in the camera and radar sensor, braking may occur unexpectedly or not at all.
Pilot Assist is designed to follow a vehicle ahead in the same lane and maintain a time interval to that vehicle set by the driver. If the radar sensor does not detect a vehicle ahead, it will instead maintain the speed set by the driver. This will also happen if the speed of the vehicle ahead exceeds the set speed for your vehicle.
- Pilot Assist can follow another vehicle at speeds from a standstill up to 200 km/h (125 mph).
- Pilot Assist can provide steering assistance from near-stationary speeds up to 140 km/h (87 mph).
Warning
- Pilot Assist is not a collision avoidance system. The driver must intervene if the system fails to detect a vehicle ahead.
- Pilot Assist does not brake for people, animals, objects, small vehicles (e.g. cycles and motorcycles), low trailers as well as oncoming, slow or stationary vehicles.
- Do not use Pilot Assist in demanding situations, such as in city traffic, at intersections, on slippery surfaces, with a lot of water or slush on the road, in heavy rain/snow, in poor visibility, on winding roads, on highway on- or off-ramps, or with a trailer connected to the vehicle.
Important
In curves and forks in the road
Pilot Assist is designed to interact with the driver. The driver should never wait for steering assistance from Pilot Assist, but instead should always be ready to increase his or her own steering efforts, particularly in curves.
- When the vehicle is approaching an off-ramp or a fork in the road, the driver should steer toward the desired lane to indicate to Pilot Assist the desired direction of travel.
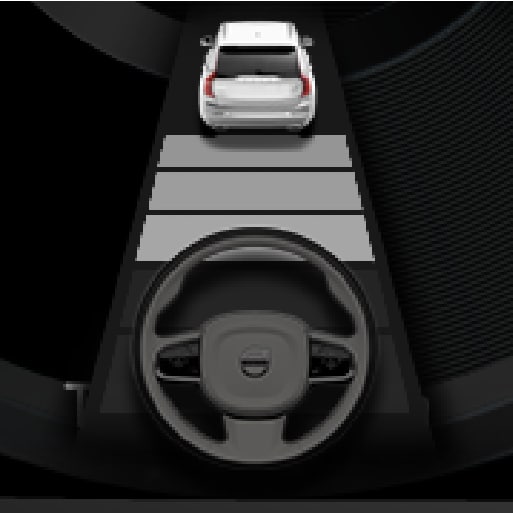
Pilot Assist strives to keep the vehicle in the center of the lane
When Pilot Assist provides steering assistance, it strives to position the vehicle in the center of the lane between the lane markings. For the smoothest driving experience possible, the driver should permit the vehicle to find the optimal positioning. The driver should check that the vehicle is positioned safely in the lane and can always adjust the vehicle's position by applying more force to the steering wheel.
- If Pilot Assist does not position the vehicle appropriately in the lane, the driver should turn off Pilot Assist or switch to Adaptive Cruise Control.
Overview
Controls
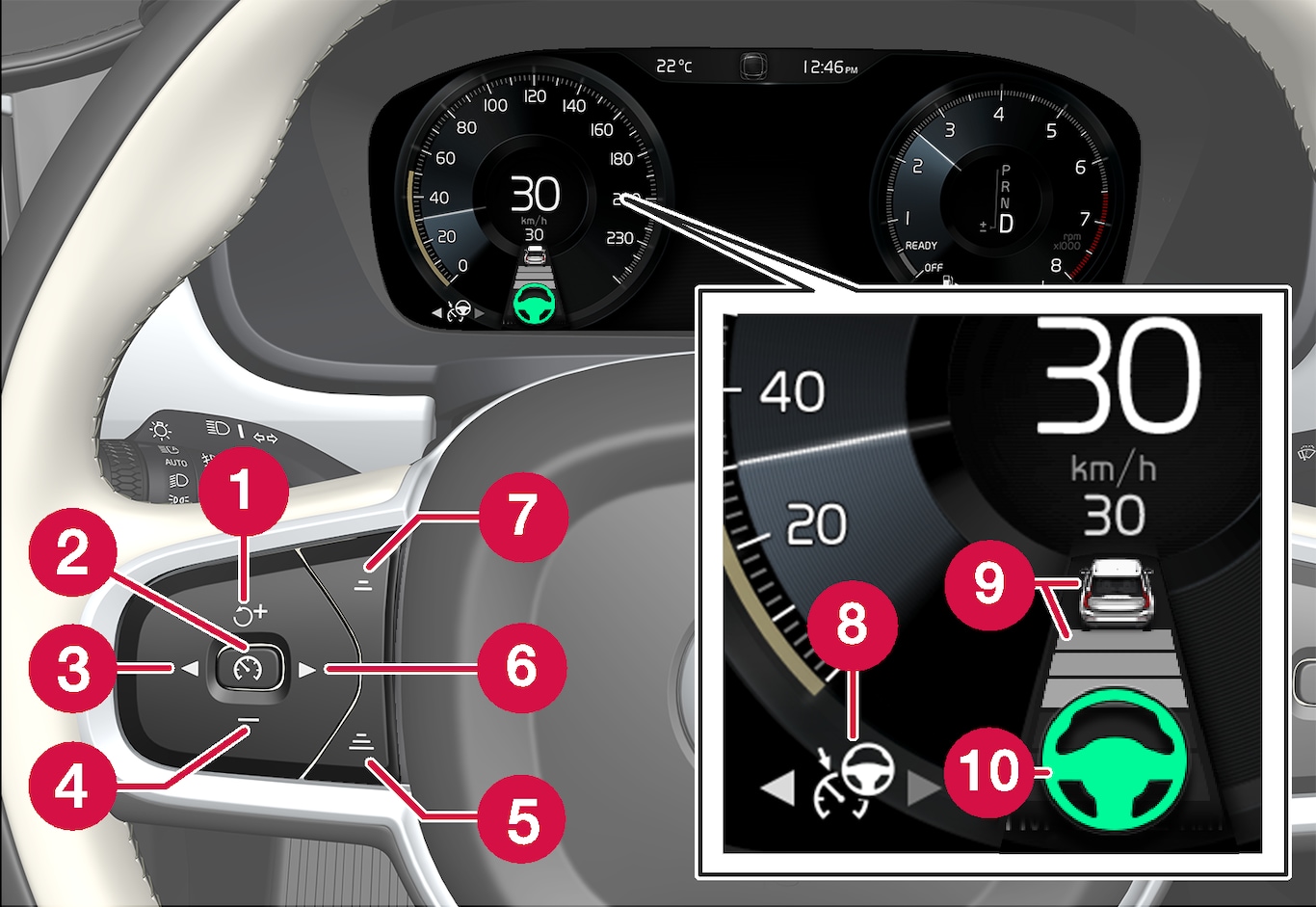
 |  : Activates Pilot Assist from standby mode and resumes the set speed and time interval : Activates Pilot Assist from standby mode and resumes the set speed and time interval |
 |  : Increases the set speed : Increases the set speed |
 |  : From standby mode - activates Pilot Assist and sets the current speed : From standby mode - activates Pilot Assist and sets the current speed |
 |  : From active mode - deactivates/puts Pilot Assist in standby mode : From active mode - deactivates/puts Pilot Assist in standby mode |
 | ◀: Switches from Pilot Assist to Adaptive Cruise Control |
 |  : Reduces the set speed : Reduces the set speed |
 | Increases the time interval to the vehicle ahead |
 | ▶: Switches from Adaptive Cruise Control to Pilot Assist |
 | Reduces the time interval to the vehicle ahead |
 | Function symbol |
 | Symbols for target vehicle and distance to the vehicle ahead |
 | Symbol for activated/deactivated steering assistance |
Instrument panel
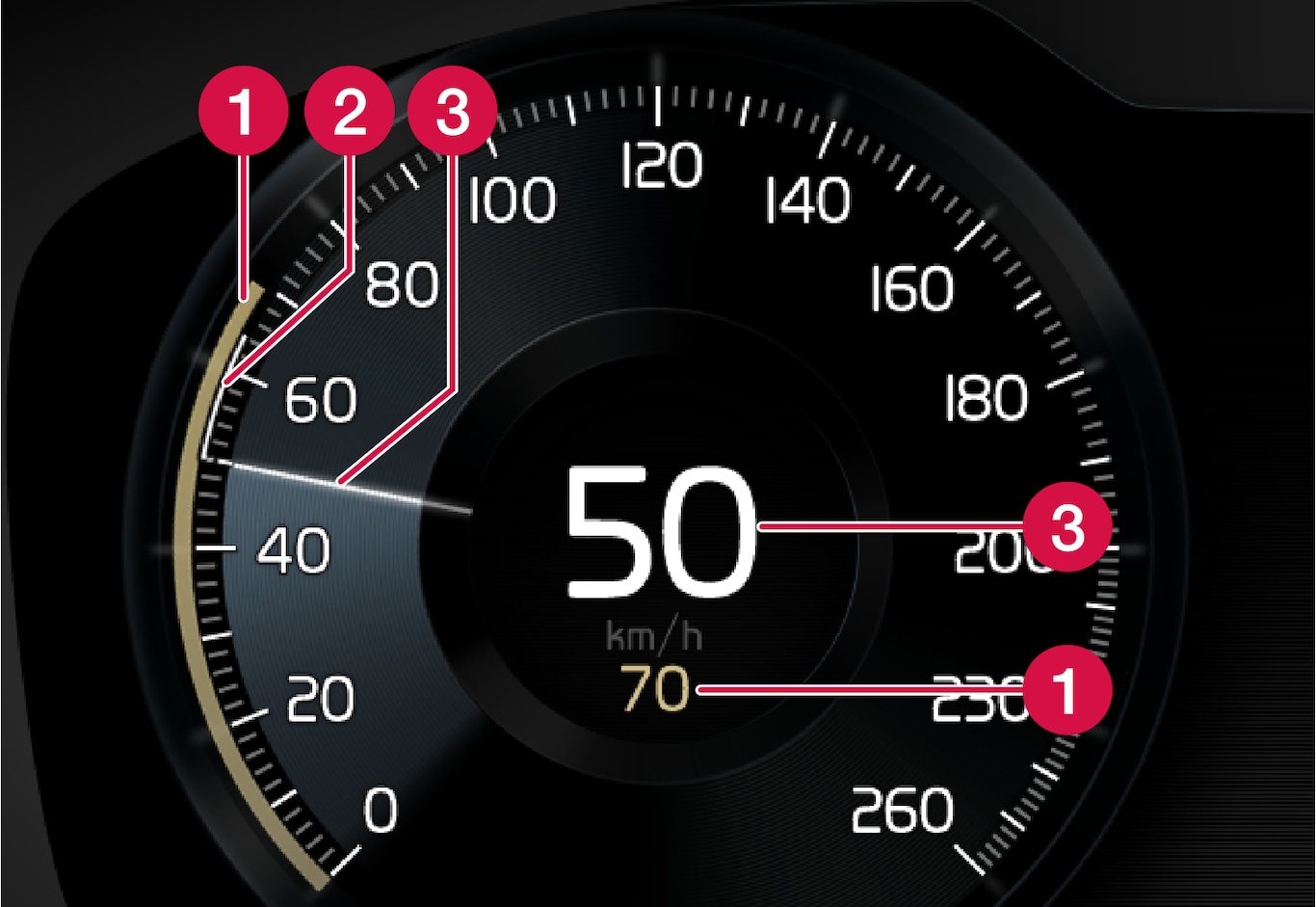
 Set speed
Set speed Speed of the vehicle ahead
Speed of the vehicle ahead The current speed of your vehicle
The current speed of your vehicle
See "Pilot Assist symbols and messages" for examples of different combinations of symbols depending on the traffic situation.