How Pilot Assist works
The Pilot Assist function is primarily intended for use on motorways and similar major roads where it can contribute to more comfortable driving and a more relaxed driving experience.
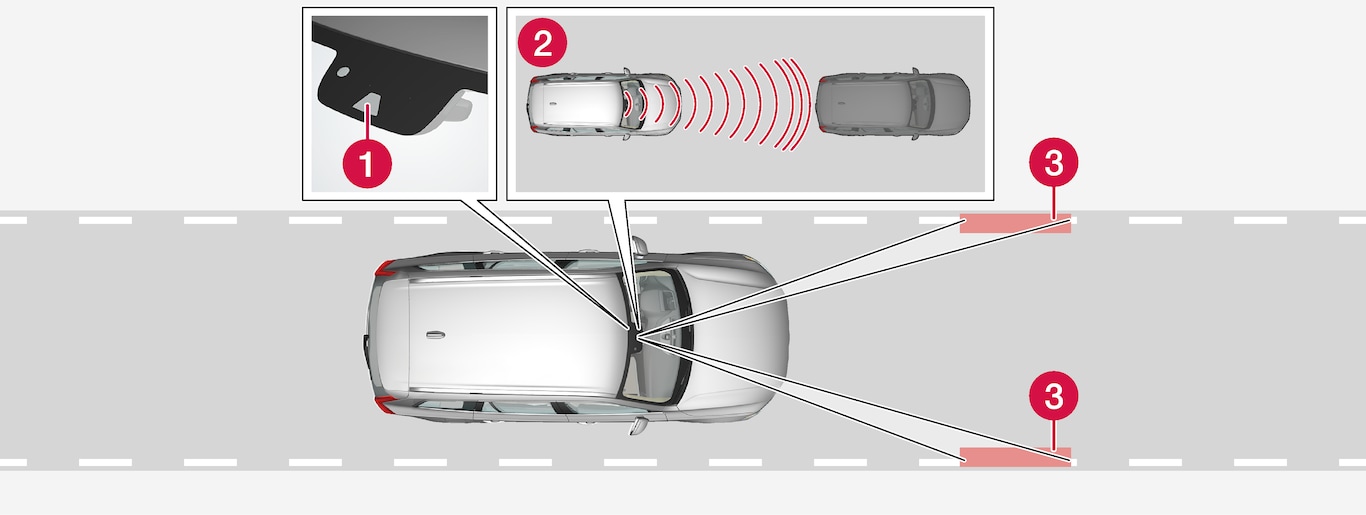
 Camera and radar unit
Camera and radar unit Distance readers
Distance readers Readers, side markings
Readers, side markings
The driver selects the desired speed and a time interval to the vehicle ahead. Pilot Assist scans the distance to the vehicle ahead and the lane's side markings on the road surface using the camera and radar unit. The preset time interval is maintained with automatic speed adjustment whilst the steering assistance helps to position the car in the lane.
Pilot Assist steering assistance takes into account the speed of the preceding car and the lane markings. The driver can at any time ignore the Pilot Assist steering recommendation and steer in another direction, e.g. to change lane or avoid an obstruction on the road.
If Pilot Assist cannot interpret the lane unambiguously, e.g. if the camera and radar unit does not see the lane's side markings, Pilot Assist temporarily deactivates steering assistance, but resumes it if the lane can be interpreted again - although the speed and distance control functions remain active.
Warning
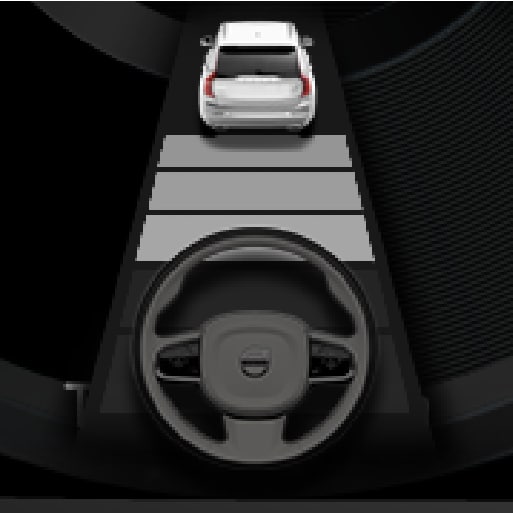

The current status of steering assistance is indicated by the colour of the steering wheel's symbol:
• GREEN steering wheel indicates active steering assistance
• GREY steering wheel (as in illustration) indicates deactivated steering assistance.
Warning
- The Pilot Assist function is supplementary driver support intended to facilitate driving and make it safer – it cannot handle all situations in all traffic, weather and road conditions.
- The driver is advised to read all sections in the Owner's Manual that relate to this function to learn about factors such as its limitations and what the driver should be aware of before using the system (see the list of links at the end of this article).
- Pilot Assist must only be used if there are clear lane lines painted on each side of the lane. All other use involves increased risk of contact with surrounding obstacles that cannot be detected by the function.
- Pilot Assist is not a substitute for the driver's attention and judgement. The driver is always responsible for ensuring the car is driven in a safe manner, positioned correctly in the lane, at the appropriate speed, with an appropriate distance to other vehicles, and in accordance with current traffic rules and regulations.
Note
Pilot Assist regulates the speed with acceleration and braking. It is normal for the brakes to emit a low sound when they are being used to adjust the speed.
Pilot Assist attempts to regulate the speed smoothly. In situations that demand sudden braking the driver must brake himself/herself. This applies in cases of large speed differences or if the car in front brakes suddenly. Due to the limitations of the camera and radar unit, braking may come unexpectedly or not at all.
Pilot Assist aims to follow the vehicle ahead in the same lane at a time interval set by the driver. If the radar unit cannot see any vehicle in front then the car will instead maintain the speed set and stored by the driver. This also takes place if the speed of the vehicle ahead increases and exceeds the stored speed.
- Pilot Assist can follow another vehicle at speeds from 0 km/h up to 200 km/h (125 mph).
- Pilot Assist can give steering assistance from almost stationary up to 140 km/h (87 mph).
- Pilot Assist can follow another vehicle at speeds from 30 km/h (20 mph) up to 200 km/h (125 mph).
- Pilot Assist can give steering assistance from 30 km/h (20 mph) up to 140 km/h (87 mph).
Warning
- Pilot Assist is not a collision avoidance system. The driver must intervene if the system does not detect a vehicle in front.
- Pilot Assist does not brake for people, animals, objects, small vehicles (e.g. cycles and motorcycles), low trailers as well as oncoming, slow or stationary vehicles.
- Do not use Pilot Assist in demanding situations, such as in city traffic, at junctions, on slippery surfaces, with a lot of water or slush on the road, in heavy rain/snow, in poor visibility, on winding roads, on slip roads, or with a trailer connected to the car.
Important
Round bends and when the road splits
Pilot Assist interacts with the driver, who should therefore not wait for the steering assistance from Pilot Assist but should always be prepared to increase his/her own steering input, especially in bends.
- When the car approaches an exit or if the lane splits, the driver should steer towards the desired lane in order to specify the desired direction to Pilot Assist.
Pilot Assist strives to keep the car in the middle of the lane
When Pilot Assist helps to steer, it strives to position the car in between the lane markings and therefore it is recommended to let the car find the optimal placement to achieve as smooth a driving experience as possible. The driver checks that the car is positioned safely in the lane, and always has the ability to adjust the position by making his/her own steering corrections.
- If Pilot Assist does not position the car in an appropriate way in the lane, it is recommended to turn Pilot Assist off or switch to Adaptive cruise control.
Overview
Controls
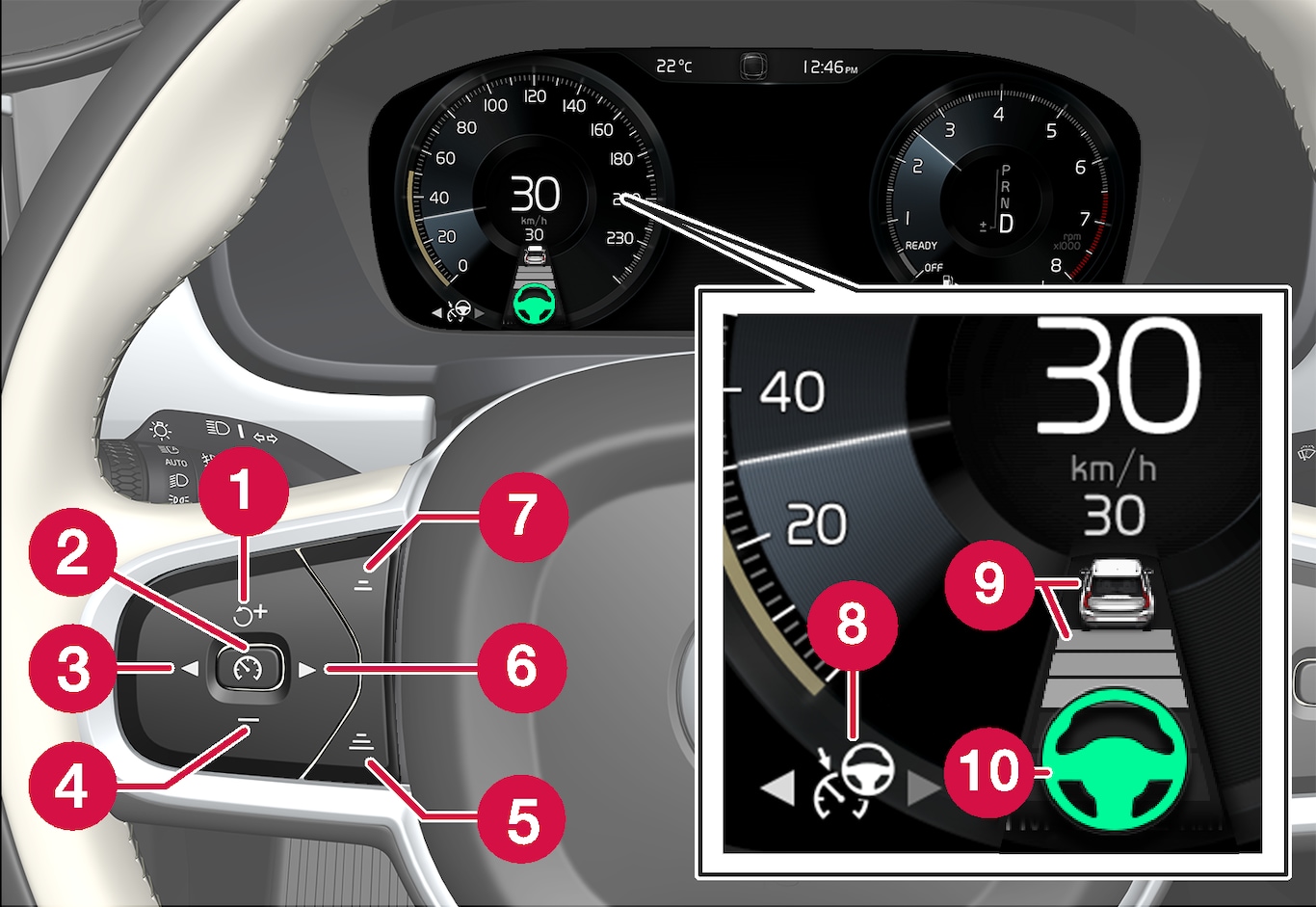
 |  : Activates Pilot Assist from standby mode and resumes the stored speed and time interval : Activates Pilot Assist from standby mode and resumes the stored speed and time interval |
 |  : Increases the stored speed : Increases the stored speed |
 |  : From standby mode - activates Pilot Assist and stores the current speed : From standby mode - activates Pilot Assist and stores the current speed |
 |  : From active mode - deactivates/changes Pilot Assist to standby mode : From active mode - deactivates/changes Pilot Assist to standby mode |
 | ◀: Switches from Pilot Assist to adaptive cruise control |
 |  : Reduces stored speed : Reduces stored speed |
 | Increases the time interval to vehicles ahead |
 | ▶: Switches from adaptive cruise control to Pilot Assist |
 | Reduces the time interval to vehicles ahead |
 | Function symbol |
 | Symbols for target vehicle and time interval to vehicles ahead |
 | Symbol for activated/deactivated steering assistance |
Driver display
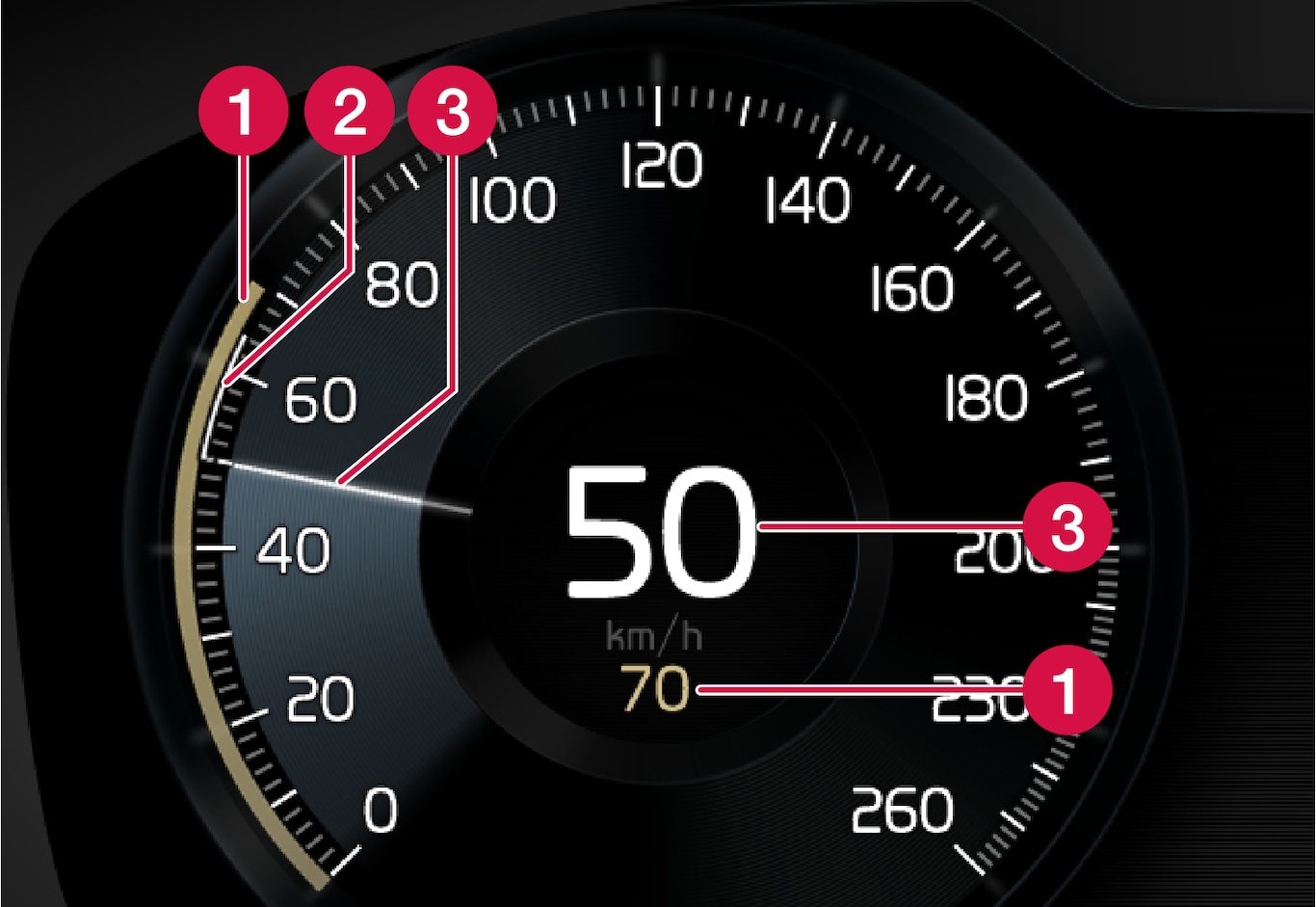
 Stored speed
Stored speed Speed of vehicle ahead
Speed of vehicle ahead Current speed of your car
Current speed of your car
To see different combinations of symbols depending on traffic situation - see the heading "Symbols and messages for Pilot Assist".