Procedure used to establish the values
The values in the table below are established in accordance with WLTP1, which is an international test method performed in a laboratory environment. The method uses drive cycles to simulate an average driving run of the car. Every drive cycle is determined by different conditions such as speed, time and mileage.
| Urban driving | Low speed |
| Suburban driving | Medium speed |
| Extra-urban driving | High speed |
| Motorway driving | Extra high speed |
Symbol explanation
This is an explanation of the symbols used in the specification table below.
 | Urban driving. |
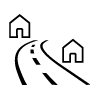 | Suburban driving. |
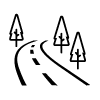 | Extra-urban driving. |
 | Motorway driving. |
 | Combined value (mixed driving). |
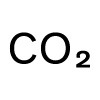 | Gram CO₂/km. |
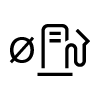 | Litre/100 km. |
 | Low value. |
 | High value. |
Specifications for fuel consumption and emissions
 |  |  |  |  | ||||||
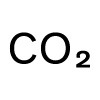 | 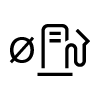 | 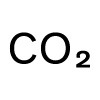 | 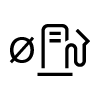 | 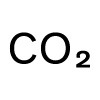 | 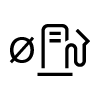 | 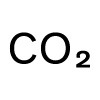 | 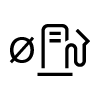 | 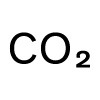 | 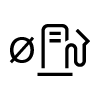 | |
 | 263 | 11.6 | 174 | 7.7 | 160 | 7.1 | 202 | 8.9 | 191 | 8.5 |
 | 277 | 12.3 | 189 | 8.4 | 174 | 7.7 | 222 | 9.8 | 208 | 9.2 |
Note
Certified values and actual values
When driving, the car's fuel consumption can differ from the certified values. Some reasons for this may be:
- Driving style.
- Extra equipment and cargo affect the car's weight or air resistance.
- Non-standard wheels can increase rolling resistance and air resistance.
- High speed causes increased air resistance.
- Road, traffic and weather conditions.
- The general condition of the car.
- Fuel grade.