The car's certified values for range and electricity consumption
These are the certified values for your car's range and use of electrical power. However, range and electricity consumption vary according to the circumstances and driving conditions. These values should not be interpreted as an expected range but should primarily be used to compare different cars.
Procedure used to establish the values
The values in the table below are established in accordance with WLTP[1], which is an international test method performed in a laboratory environment. The method uses drive cycles to simulate an average driving run of the car. Every drive cycle is determined by different conditions such as speed, time and mileage.
| Urban driving | Low speed |
|---|---|
| Suburban driving | Medium speed |
| Extra-urban driving | High speed |
| Motorway driving | Extra high speed |
Symbol explanation
This is an explanation of the symbols used in the specification table below.
 | Certified value for the car's potential range (km)[2]. |
 | Urban and suburban driving. |
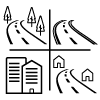 | Average value over all four drive cycle phases (urban, suburban, extra-urban and motorway driving). |
 | Certified value for the car's electricity consumption (kWh/100 km). The value is an average over all four drive cycle phases (urban, suburban, extra-urban and motorway driving). |
 | Low value. |
 | High value. |
Specifications for range and electricity consumption
 |  | ||
 |  | ||
 | 771 | 618 | 19.4 |
 | 646 | 521 | 22.8 |
If data is missing in the table, it will be updated at a later date.Note
Certified values and actual values
- Driving style.
- Extra equipment and cargo affect the car's weight or air resistance.
- Non-standard wheels can increase rolling resistance and air resistance.
- High speed causes increased air resistance.
- Road, traffic and weather conditions.
- The general condition of the car.