Limitations of Cross Traffic Alert1
The CTA2 function with auto-brake may have limited functionality in certain situations. Brake intervention is active at speeds below 15 km/h.
CTA does not perform optimally in all situations but has some limitations. For example, the CTA sensors cannot "see" through other parked vehicles or obstructing obstacles.
Here are some examples of situations where CTA’s "field of vision" may be already limited and approaching vehicles cannot therefore be detected until they are very close:
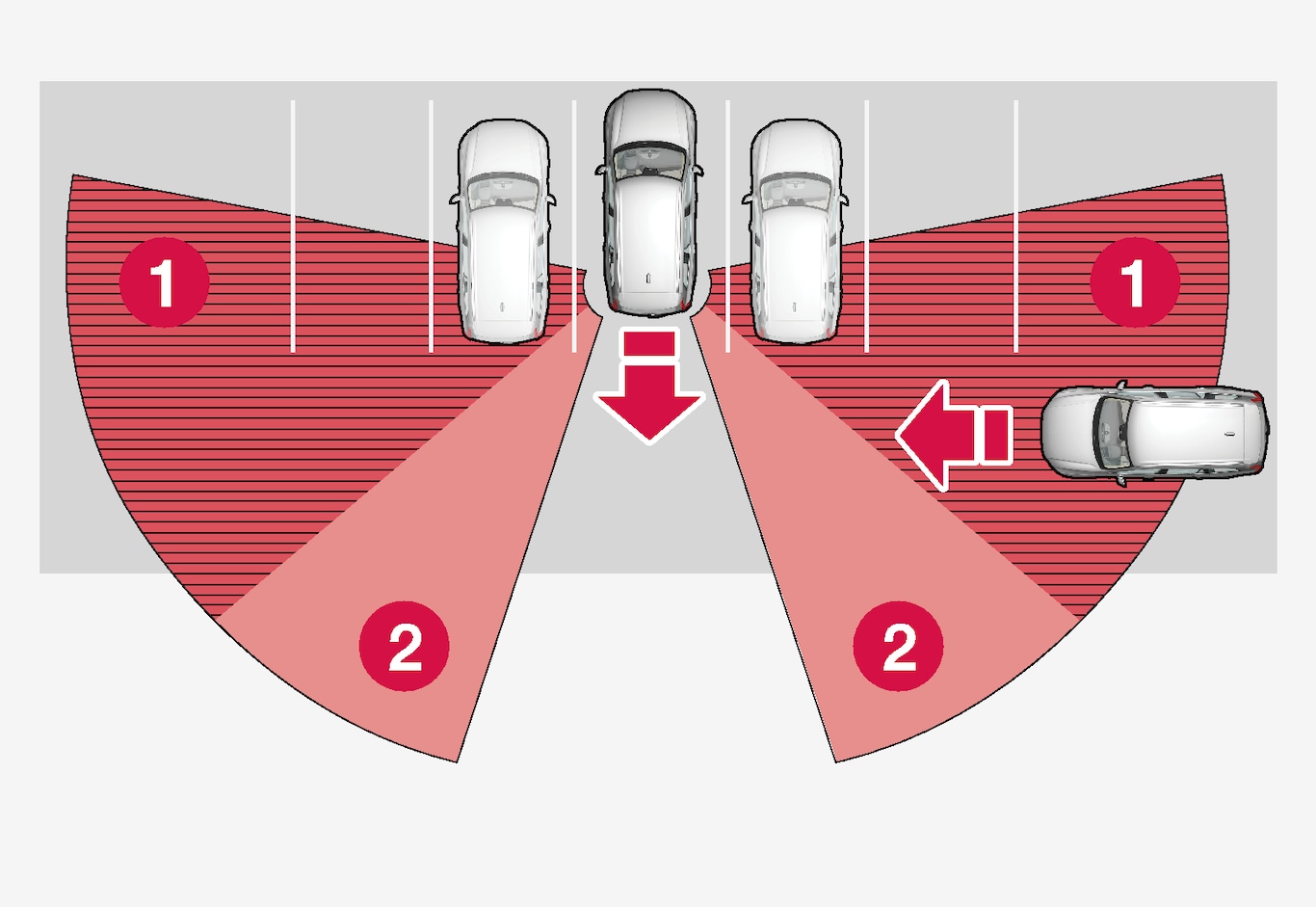
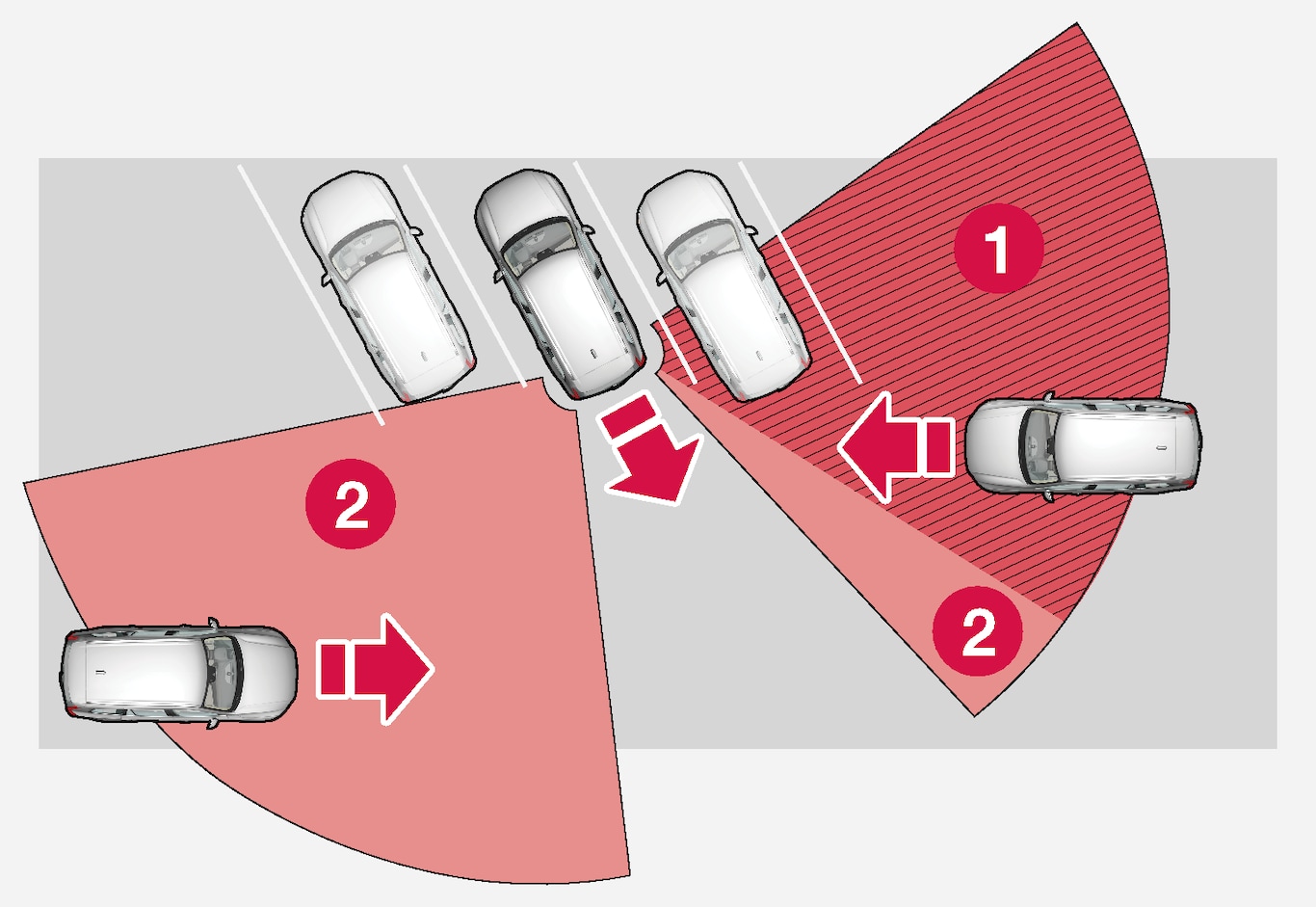
 Blind CTA sector.
Blind CTA sector. Sector in which CTA can detect/“see”.
Sector in which CTA can detect/“see”.
However, as your car slowly reverses, the angle it makes with the obstructing vehicle/object changes and the blind sector rapidly decreases.
Examples of further limitations
- The auto-brake subfunction only detects moving vehicles and therefore cannot "see" and brake for stationary obstacles, a cyclist or a pedestrian, for example.
- Dirt, ice and snow covering the sensors may reduce the functions and deactivate alerts.
- CTA is automatically deactivated if a trailer, bicycle rack or similar is connected to the car's electrical system.
- For optimal performance of CTA, no bicycle rack, luggage carrier or similar should be mounted on the car's towbar.
Note
This function uses the car's camera and radar units, which have certain general limitations.